혀 내밀 때와 큰 혀, Protruding tongue and big tongue
|
다음은 “혀를 내밀어요.”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 혀를 내밀어요
Q.
3개월 된 남자아이 엄마입니다.
우리 애기가 혀를 잘 내미는데요.
아마도 태어나서 얼마 되지 않아서부터 그랬던 것 같습니다.
괜찮은 건지요?
그리고 다른 곳도 보지만 위쪽을 많이 보는 편이 거든요.
혹 위의 질문과 관련이 있는지, 아님 다른 건지 궁금합니다.
답변 부탁드립니다.
A.
여숙님
안녕하십니까. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다.
자녀의 나이와 성별, 과거 현재 가족의 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견, 적절한 임상검사 등의 결과를 종합해서 진단 치료하는 것이 이상적이지만 주신 정보를 참작해서 답변을 드립니다.
아이들의 혀를 내미는 원인은 다음과 같습니다.
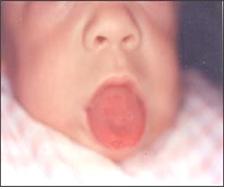
그림 3-35. 선천성 갑상선 기능저하증으로 혀를 비정상으로 내밀고 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
① 혀의 크기는 정상인데 입안의 크기가 비정상적으로 작을 때
② 입안의 크기는 정상인데 혀의 크기가 비정상적으로 너무 클 때
③ 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증이 있는 신생아, 영유아
④ 알레르기 비염이 있거나
⑤ 어떤 원인으로 콧구멍과 비강을 통해 숨을 제대로 쉬지 못할 때
⑥ 아데노이드가 비정상적으로 비대 되어 상기도가 막힐 때
⑦ 저능아
⑧ 당뇨병을 앓는 엄마로부터 태어난 신생아
⑨ 소토스 증후군(Sotos syndrome)
⑩ 베크위트–비드만 증후군(Beckwidth Wiedemann syndrome)-선천성 과대 혀, 거체구증과 복벽 결손 그리고 신생아 저혈당을 동반하는 증후군
⑪ 그 외 원인으로 혀를 잘 내밀 수 있고 혀가 클 수 있습니다.
⑫ 건강하고 정상적인 신생아, 영유아, 학령기 아이들도 때로는 버릇으로 혀를 내밀 수 있습니다.
가장 흔한 혀 내미는 원인은 정상으로 성장 발육하면서 가끔 혀를 내미는 버릇입니다.
영아의 주위환경, 영아가 뉘어 있는 자세 등으로 한쪽 방향만 일시적으로 보는 영아들도 있습니다. 걱정하실 것 없는 것 같습니다.
정기 건강검진을 받으러 소아청소년과에 가실 때 그런 것에 대해 의사 선생님과 상담하시기 바랍니다.
정기 건강검진을 받으러 가시기 전에 궁금한 사항을 메모해 두셨다가 가지고 가시면 좋을 것입니다.
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호 백과]-제 3권 신생아, 영유아, 학령기와 사춘기 아이들의 성장발육–생후 1개월~6세 영유아들의 발육 이정표, 나이에 해당하는 성장 발육, 제 15권 소아청소년 알레르기 및 면역질환–알레르기 비염 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다. 질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주세요. 감사합니다.이상원 드림
|
다음은 “혀가 항상 나와 있어서요.”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 혀가 항상 나와 있어서요
Q.
안녕하십니까? 돌 지난 여자아입니다. 신생아 때부터 항상 혀가 좀(0.5~6cm) 나와 있습니다.
물론 입에 뭐가 들어 있으면 다물지만요. 잠잘 때도 마찬가지구요. 소아청소년과에서는 아랫 턱이 좀 짧은 거 같다는 말씀만 하시구 별 말씀을 안 하시네요. 치과에 인터넷 상담을 했더니 소아청소년과 에 문의하라구 하시구요. 정확한 진단을 해봐야 하나요? 한다면 어느 과에서 해야 하는지요.
그리고 아직 아랫니 2개밖에 안 났는데 이것도 영향이 있는 걸까요?
이럴 경우 차후에 말하거나 미관상 문제는 없을까요? 답변 부탁드립니다.
A.
걱정님
안녕하세요. 좋은 질문을 해주셔 감사합니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등 자세한 정보가 있을수록 보다 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있지만 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답하겠습니다.
글쎄요. 그 동안 고명하신 소아청소년과 전문의와 인터넷 그리고 다른 참고서를 통해 많이 알아보셨는데 제가 인터넷으로 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있을까 걱정됩니다.
혀의 크기는 정상이지만 입 안의 크기가 정상보다 작으면 혀가 입 밖으로 나올 수 있습니다. 입의 크기는 정상이지만 혀 크기가 비정상적으로 더 크면 혀가 입 밖으로 나올 수 있을 것입니다.
피에르 로빈 증후군(Pierre Robin’s syndrome)이 있는 신생아, 영유아는 아래턱이 정상보다 훨씬 작습니다.
그래서 혀가 입 밖으로 쉽게 나올 수 있습니다.
알레르기 비염으로 코가 막히면 입을 벌리고 입으로 숨을 쉬는 구강호흡을 합니다.
이때도 혀를 입 밖으로 잘 내밉니다.
또 정상적인 크기의 혀가 입 밖으로 조금 내밀 수도 있습니다.
그 외에 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증이 있을 때도,
또 저능아가 혀를 밖으로 내밀 수도 있습니다.
그 외 혀 속에 선천성 혈관이상, 종양, 혀 근육이상, 후를러 증후군 등으로 혀가 비정상적으로 커질 수 있고 혀를 입 밖으로 내밀 수 있습니다.
그와 혀의 관계에 대해서는 잘 모르겠습니다.
구강호흡을 장기간 계속 하면 입안의 전체 해부학적 구조에 변화가 자연적으로 생길 것입니다. 계속 걱정이 되시면 소아청소년과에서 진찰 진단을 받으시고 그 문제에 관해 다시 상담하시기 바랍니다.
치과의와 구강 전문의를 소개해 달라고 하세요. 질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Protruding tongue and big tongue
The following is an example of a Q&A for health counseling for children and adolescents on the Internet about “stick out your tongue.”
Q&A. stick out your tongue
Q.
I am a mother of a 3-month-old boy. My baby sticks out his tongue. She’s probably been like this not long after she was born. Are you okay? And I look at other places, but I tend to look upwards a lot. I wonder if this is related to the above question or if it is something else. please answer my question.
A.\
Lady Hello. Thanks for asking. It is ideal to diagnose and treat the results of the child’s age and gender, past and present family history, symptom signs and examination findings, and appropriate clinical tests, but we will give you an answer taking into account the information you have given us. Causes of sticking out the tongue in children include:

Figure 3-35. The tongue is sticking out abnormally due to congenital hypothyroidism. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
① When the size of the tongue is normal but the size of the mouth is abnormally small
② When the size of the mouth is normal but the size of the tongue is abnormally large
③ Newborns and infants with congenital hypothyroidism
④ Have allergic rhinitis
⑤ When you cannot breathe properly through your nostrils and nasal passages for some reason ⑥ When the adenoids are abnormally enlarged and the upper airway is blocked
⑦ a blind child
⑧ Newborns born to mothers with diabetes
⑨ Sotos syndrome ⑩ Beckwidth Wiedemann syndrome – Syndrome with congenital oversized tongue, macrocytosis and abdominal wall defects, and neonatal hypoglycemia
⑪ For other reasons, the tongue may stick out well and the tongue may be large.
⑫ Healthy, normal newborns, toddlers, and school-age children can sometimes habitually stick their tongue out. The most common cause of tongue sticking is the habit of occasionally sticking out the tongue during normal growth and development. Some infants temporarily see only one direction due to the infant’s surroundings or the infant’s lying position. There seems to be nothing to worry about.
When you go to the Department of Pediatrics for regular health checkups, please consult your doctor about such matters. It would be a good idea to write down any questions you have before going for a regular health check-up and take it with you.
www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume 3 Growth and Development of Newborns, Infants, School-age and Adolescent Children – Milestones in the development of infants and toddlers aged 1 month to 6 years, growth and development corresponding to their age, Vol. 15 Please refer to Allergy and Immune Disease-Allergic Rhinitis in Children and Adolescents. If you have any more questions, please contact us again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won .
The following is an example of a Q&A for health counseling for children and adolescents on the Internet about “the tongue is always out.”
Q&A. tongue is always out
Q.
Hello? It’s a past girl. The tongue is always protruding a little (0.5-6 cm) since newborn. Of course, if you put something in your mouth, you close it. The same goes for sleeping. The Department of Pediatrics only says that the lower jaw is a bit short, but doesn’t say much. When I consulted the dentist online, they asked me to contact the Department of Pediatrics.
Do I need to make an accurate diagnosis? If so, in which department? And I still only have 2 lower teeth, is this having an effect? In this case, will there be any issues with the appearance or later? please answer about my question.
A.
don’t worry Good morning. Thanks for asking a good question. The more detailed information such as the child’s age, gender, past medical history, family history, examination findings, and clinical examination, the better we can give you a better answer, but we will answer based on the information you have given us.
I do not know. You’ve learned a lot from famous pediatricians, the Internet, and other reference books. The size of the tongue is normal, but if the size inside the mouth is smaller than normal, the tongue may stick out of the mouth. The size of the mouth is normal, but the tongue may stick out of the mouth if it is unusually large.
Newborns and infants with Pierre Robin’s syndrome have a lower jaw that is much smaller than normal. So the tongue can easily come out of the mouth. If your nose is blocked due to allergic rhinitis, open your mouth and breathe through your mouth. Again, stick your tongue out of your mouth.
Also, a normal-sized tongue may stick out a little out of the mouth. In addition, when there is congenital hypothyroidism,
A child with a disability may also stick their tongue out. In addition, due to congenital blood vessel abnormalities in the tongue, tumors, tongue muscle abnormalities, Hurler syndrome, etc., the tongue may become abnormally enlarged and the tongue may stick out of the mouth. I’m not sure about his relationship with the tongue.
If you continue to breathe through your mouth for a long time, changes will naturally occur in the overall anatomy of your mouth. If you are still concerned, please consult the Pediatrics Department for a diagnosis and discuss the matter again. Ask for referrals to dentists and oral specialists. If you have more questions, please feel free to contact us again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.