입 냄새(구취), Halitosis
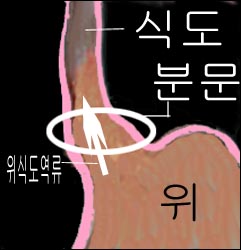
그림 174. 위식도 역류 병이 있을 때도 입냄새가 날 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 입에서 고약한 냄새가 나는 증상을 입 냄새(Halitosis)라고 한다.
- 입 냄새는 어떤 병이 아니고 어떤 원인으로 생기는 일종의 증상이다.
- 입 냄새는 영아들이나 유아들에게는 잘 생기지 않는다.
- 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들 또는 성인들에게 드물게 생길 수 있다.
- 입 냄새가 나면 때로는 대인 관계에도 문제가 될 수 있다.
- 대부분의 경우 원인은 확실히 모른다.
- 유아들에게 헤르페스바이러스 치은구내염 (헬퍼스바이러스 치은구내염)이 입안에 있을 때 입 냄새가 심하게 날 수 있다.
- 심한 충치, 고름나는 치수 염, 아주 심한 치은염, 궤양성 치은염, 만성 편도염, 만성 아데노이드염, 폐 질환, 위장 질환, 위식도 역류, 탈수증, 어떤 약물 복용, 양파, 마늘, 파 등 냄새나는 음식물을 먹었을 때, 그 외의 다른 원인으로 입 냄새가 날 수 있다.
- 병력, 진찰 등을 종합해서 원인을 찾고 원인에 따라 치료한다.
- 요즘 만성 편도염이나 만성 아데노이드염으로 생기는 성인 입 냄새는 레이저로 치료하기도 한다.
- 소아 경우, 레이저로 치료하지 않는다.
|
다음은 “9개월 된 아기의 입 냄새”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 9개월 된 아기의 입 냄새
Q.
울 아기가 침을 많이 흘리는데요. 가제수건이나 실리콘 칫솔로 하루에 한두 번 입을 닦아 주거든요. 근데 시큼한 침 냄새가 나서 어디 이상이 있는 건 아닌지 궁금하네요. 큰애는 하루에 한 두 번 닦아주어도 입 냄새는 안 났는데 이상하네요. 병원에를 가봐야 하는 건지…
또 응아를 이틀에 한 번 정도 하는데 변이 단단해서 응아할 때 많이 웁니다.
어떻게 아이한테 해주어야 할지요..
A.
정아님
안녕하십니까. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다.
자녀의 나이와 성별, 과거 현재 가족의 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견, 적절한 임상검사 등의 결과를 종합해서 진단 치료하는 것이 이상적이지만 주신 정보를 참작해서 답변을 드립니다.
방금 입 냄새에 관한 질문이 있어서 답변을 해 드리고 입 냄새에 관한 글을 의학 포럼에 올렸습니다.
9개월 된 영아의 입안을 들여다보시면 잇몸, 입천장, 혀, 인두 등이 참 생생하고 건강하고 깨끗할 것입니다.
시큼한 입 냄새는 아마도 위식도 역류나 소화가 잘 되지 않아 생긴 것일 겁니다.
변비가 있고 입 냄새가 있는 것은 우유나 우유가 들은 음식물 1~2주 동안 먹이지 마시고 입 냄새가 그래도 나는지 관찰해보세요.
손전등 빛으로 비추고 입안을 들여다보시면 영유아들은 자연적으로 침이 많이 분비되어 자가 구강 청결이 됩니다.
그래서 입안은 닦아줄 필요가 없습니다. 변비증, 입 냄새 참조.
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호 백과]-제 22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요–변비 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다. 계속 냄새가 나고 변비가 있으면 자녀 단골 의사와 상담하시기 바랍니다. 질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주세요. 감사합니다. 이상원.
Badmouth smell (halitosis)

Figure 174. Bad breath can also occur with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Bad odor from the mouth is called Halitosis.
• Bad breath is not a disease but a symptom caused by some cause.
• Bad breath is less common in infants and young children.
• It can occur rarely in school-age children, adolescents or adults.
• Bad breath can sometimes be a problem with relationships.
• In most cases, the cause is unknown.
• Infants may have bad breath when herpesvirus gingivostomatitis (herpesvirus gingivostomatitis) is in their mouth.
• Severe dental caries, pus pulpitis, very severe gingivitis, ulcerative gingivitis, chronic tonsillitis, chronic adenoiditis, lung disease, gastrointestinal disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, dehydration, taking any medications, or eating smelly foods such as onions, garlic, and green onions. When ingested, bad breath may be caused by other causes.
• Comprehensive medical history and examination to find the cause and treat according to the cause.
• Nowadays, the bad breath in adults caused by chronic tonsillitis or chronic adenoiditis is sometimes treated with a laser.
• In children, do not treat with laser.
The following is an example of a Q&A for health counseling for children and adolescents on the Internet about “the bad breath of a 9-month-old baby”.
Q&A. 9-month-old baby’s breath
Q. My baby is drooling a lot. I clean my mouth once or twice a day with a gauze towel or a silicone toothbrush. But it smells like sour saliva, so I’m wondering if there’s something wrong with it. The eldest one didn’t smell bad even after wiping once or twice a day, which is strange. Do I have to go to the hospital… Also, I vomit about once every two days, but my stools are hard, so I cry a lot when I vomit. How should I do it to my child? A.
Ahn Jung Hello.
Thanks for asking. It is ideal to diagnose and treat the results of the child’s age and gender, past and present family history, symptom signs and examination findings, and appropriate clinical tests, but we will give you an answer taking into account the information you have given us. I just had a bad breath question, and I’ve answered it and posted an article about bad breath on the medical forums. If you look into the mouth of a 9-month-old infant, the gums, roof of the mouth, tongue, and pharynx will be vivid, healthy and clean.
The sour breath is probably due to gastroesophageal reflux or poor digestion. If you are constipated and have bad breath, do not feed milk or food containing milk for 1 to 2 weeks and observe if the bad breath still persists.
If you shine it with a flashlight and look into your mouth, babies and toddlers naturally secrete a lot of saliva to clean their mouths. So there is no need to wipe your mouth. See also constipation, bad breath.
www.drleepediatrics.com]-Volume 22, Raise Your Sons and Daughters with So Much Love-Constipation, etc. If the smell persists and you are constipated, consult your child’s regular doctor. If you have any more questions, please contact us again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine